Are Gymnosperms Vascular Or Nonvascular
Vascular Plants, also known as Tracheophyta, are a diverse group of terrestrial plants with vascular bundles tissues that transport water and nutrients throughout the constitute.
Check out awesome, educational VR rooms on Inspirit's mobile app (available for iOS and Android devices)🤩
Introduction:
Vascular plants are also called tracheophytes. Tracheophyta is derived from the Greek discussion trachea, which means a duct–a channel in plants. The vascular plants are well-ordered, as are the land plants, including blooming vascular plants and ferns. They have developed a sophisticated network of vascular systems that run throughout the constitute body, allowing for the efficient transfer of water, nutrients, and signals.
Vascular plants are avant-garde and well-developed plants that include ferns, seed plants, angiosperms, and gymnosperms. Vascular tissues of vascular plants include the xylem and phloem, which convey water and integrate nutrient, respectively.
Features of Vascular Plants
The backdrop of vascular plants are determined by their architecture; nevertheless, the presence of vascular tissues in the plants is the virtually of import feature of a tracheophyte. Other mutual qualities or backdrop of vascular plants include:
- As previously stated, vascular plants have vascular tissues and vascular bundles (xylem and phloem). These specialized structures permit vascular plants to abound in size.
- The reproduction includes generational alternation, with sporophyte as the generation face up and gametophyte as the generation back.
- Most all vascular plants have existent leaves, stems, and roots; nonetheless, certain vascular plants may have decreased features.
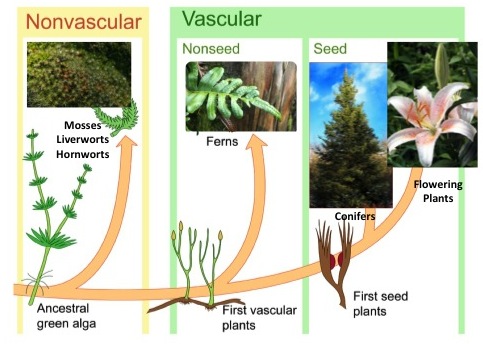
Vascular and Nonvascular plants
 Source
Source
- The primary distinction betwixt vascular and nonvascular plants is that vascular arteries ship water and nutrient to all establish areas.
- The phloem is the vessel that delivers nutrient, whereas the xylem transports water.
- A nonvascular plant, on the other mitt, lacks a vascular arrangement. This implies that nonvascular plants are significantly smaller than vascular plants, and this is one of the simplest methods to tell the difference between the ii.
- Another distinction is that a nonvascular plant lacks roots, but a vascular establish does. On the other hand, a nonvascular institute possesses rhizoids, which are tiny hairs that maintain the institute in place.
- The roots of a vascular establish offer back up and absorb h2o from the environs.
- Nonvascular plants are near typically establish in damp conditions, where they receive acceptable h2o without relying on roots.
- Nonvascular plants take simpler reproductive techniques than vascular plants. Most nonvascular plants reproduce asexually past creating single-celled spores or asexually through vegetative propagation, in which a new plant develops from a piece of the original plant.
- Vascular plants include club mosses, horsetails, ferns, gymnosperms, and angiosperms (flowering plants).
- Mosses, liverworts, and hornworts are three nonvascular constitute examples with flattened, greenish plant bodies.
Examples of Vascular Plants

Ferns
- A fern is an instance of a lower tracheophyte with a special conductive tissue called xylem and phloem that allows the flow of h2o, minerals, and food particles.
- These are non-flowering vascular plants with genuine stems, roots, and leaves that reproduce through spores.
- These plants have distinct environments, morphologies, and reproductive systems.
- Ferns like wet, warm conditions, and their numbers drib as altitude and moisture levels rise.
- Ferns are of import in ecological succession considering they grow in exposed rock cracks and marshy areas earlier woody growth.
- Due to these plants' ability to disseminate spores, generate gametes, and cocky-fertilize, long-distance dispersion is possible.
Cycad
- Cycads are non-flowering vascular plants with formed roots, stems, leaves, and vascular systems.
- These are massive trees that may achieve three to five feet in height and have woody stems.
- These plants are common in forests, only they are likewise grown past farmers for timber and animal feed.
- Female plants produce seed cones rather than a cluster of leaf-life structures holding seeds, making these plants deciduous and unusual among gymnosperms.
- Cycads such as C. circinalis and C. beddomei are planted as cute gardens.
- Cycads are sometimes known as sago palms because some species produce starch called sago from their stems.
- The leaves are often utilized in flower arrangements and other ornamental reasons.
Conclusion:
- Vascular plants are sophisticated plants with a transportation function via xylem and phloem.
- The 2 forms of vascular tissue — xylem and phloem, ship h2o, minerals, and photosynthetic products throughout the plant.
- An vascular plant, as opposed to a nonvascular constitute, may grow significantly larger.
FAQs:
1. Do vascular plants take roots?
Vascular plants are known as tracheophytes. The xylem and phloem are vascular tissues, and they enable plants to grow tall in the air without becoming wilted. Vascular plants contain roots, stalks, and leaves besides.
2. What are the 3 types of vascular plants?
Vascular plants include ferns, gymnosperms, and flowering plants. These plants have genuine stems, leaves, and roots considering they take vascular tissues.
three. Is kokosnoot tree a vascular plant?
The stem tissue of the kokosnoot palm is a complicated fibrovascular organization composed of fibrovascular bundles embedded in parenchymatous basis tissue.
four. What is the simple definition of a vascular found?
A tracheophyte is whatever of several plants that take specialized vascular tissue. The ii forms of vascular tissue, xylem and phloem, transport water, minerals, and photosynthetic products throughout the establish.
5. Give some examples of vascular and nonvascular plants.
Mustard, maize, cycad, rose, ferns, clubmosses, grasses are examples of vascular plants. On the other hand, algae, moss, hornwort, and liverwort are examples of nonvascular plants.
half dozen. Is a rose a vascular plant?
Yes, Rose is a vascular plant.
We promise you enjoyed studying this lesson and learned something cool about Vascular Plants! Join our Discord customs to go any questions yous may accept answered and to engage with other students merely like you! Don't forget to download our App to experience our fun, VR classrooms - we promise, it makes studying much more fun! 😎
Sources:
- Vascular Plants. https://www.ck12.org/assessment/tools/geometry-tool/plix.html?eId=SCI.BIO.613&questionId=54931173da2cfe5ac1c86bbb&artifactID=1914501&conceptCollectionHandle=life-scientific discipline-::-vascular-plants&collectionCreatorID=3&plix_redirect=one Accessed 10 December, 2021.
- Life Cycle of Seedless Vascular Plants. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-2.0/section/9.nineteen/main/lesson/life-cycle-of-seedless-vascular-plants-bio/ Accessed x Dec, 2021.
- Vascular Plants. https://flexbooks.ck12.org/cbook/ck-12-biology-flexbook-two.0/section/9.8/chief/lesson/vascular-plants-bio/ Accessed 10 December, 2021.
Are Gymnosperms Vascular Or Nonvascular,
Source: https://www.inspiritvr.com/general-bio/plants/vascular-plants-study-guide
Posted by: pennysperse.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Are Gymnosperms Vascular Or Nonvascular"
Post a Comment